Guest Post by the SMARTTECH3D Team
Measuring the world around us has evolved from simple hand tools to sophisticated optical 3Dtechnology. Whether it is documenting a delicate museum artifact or ensuring an engine component is built to within a few microns of its design, modern metrology relies on structural light scanners like those developed by SMARTTECH3D. To truly understand how this technology works, one must look at the two fundamental pillars of 3D imaging: accuracy and resolution.
Moving Beyond Traditional Measurement
For a long time, the industry relied on manual tools such as calipers or large Coordinate Measurement Machines (CMMs). While these “old school” methods are reliable for certain tasks, they have significant drawbacks. Traditional tools are often slow because they measure one point at a time and require physical contact with the object, which risks damaging sensitive surfaces. Furthermore, they demand high levels of expertise to operate correctly.

In contrast, 3D scanning has become the modern standard by offering a non-contact solution that captures millions of data points almost instantly. This process creates a “3D Digital Twin,” a complete virtual replica of the object that provides much more information than the limited measurements gathered by manual tools. Because the system is largely automated and intuitive, it removes much of the difficulty and human error associated with traditional metrology.
Accuracy Versus Resolution
The terms “accuracy” and “resolution” are frequently used interchangeably, but they represent two distinct concepts in the world of 3D scanning.
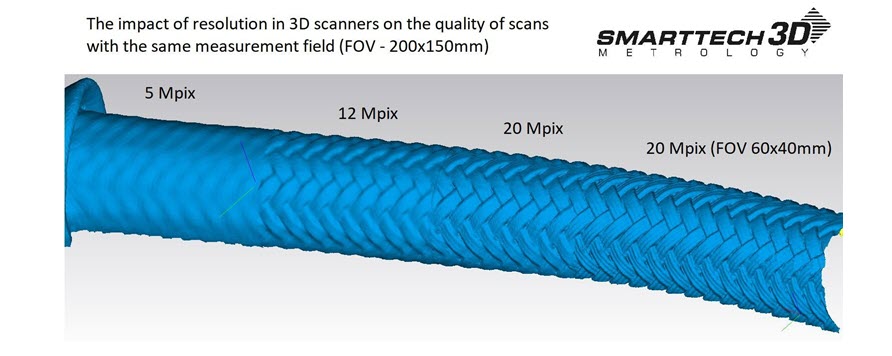
Resolution refers to the level of detail or the density of the dots within the digital model. You can think of it as the distance between two measurement points. A helpful guideline is the “Rule of 10,” which suggests that to properly map a 1 mm feature, you need a point every 1/10th of a millimeter, resulting in at least 100 points per square millimeter. High resolution is the key when the goal is to capture sharp edges and small details of parts (for example turbine blades),as well as capturing organic textures. SMARTTECH3D has the highest resolution 3D scanner on the market: SMARTTECH3D PRO 20 MP with a resolution the density of points over 1300 points per mm2 (150 mm x 100 mm FOV).
Additionally, SMARTTECH3D has a dedicated 3D scanner model named MICRON3D COLOR stereo, which is meant for digitization of valuable artifacts and museum pieces. It is characterized by its high resolution, that is able to capture even the slightest scratch as well as life-like color capture.
Accuracy, on the other hand, represents the “truth” of the measurement. It describes how closely the digital scan matches the actual physical dimensions of the object. To ensure reliability, systems undergo rigorous testing based on international standards like VDI/VDE 2634. High accuracy is the gold standard for industrial manufacturing, quality control, and reverse engineering, where even a tiny deviation from the original design can lead to mechanical failure.


The Power of Structural Light
The technology behind SMARTTECH3D scanners involves projecting specific light patterns onto a surface to map its geometry. This structural light approach offers several advantages, such as the ability to digitize entire objects in seconds. Because the process is automated, it eliminates the “shaky hand” factor that can ruin manual measurements. Additionally, these systems can capture high-resolution color and texture, a feature many industrial scanners lack, making them ideal for creating lifelike digital archives.
Real-World Uses and the Path Forward

The applications for this technology are vast and varied. In manufacturing, it is used to check engine parts for errors before they leave the factory. In archaeology, it allows researchers to create non-invasive digital twins of fragile fossils or ruins, preserving history without touching the original site. In the healthcare sector, high-accuracy scans allow for the creation of dental implants and prosthetics that are perfectly tailored to a patient’s unique anatomy.

Looking to the future, 3D scanning is becoming even more intelligent. Artificial intelligence is now being integrated to automatically clean and process scan data, while robotic arms are being used to perform 24/7 quality inspections on factory floors. As these tools become lighter and more portable, they are moving out of the lab and into the field, allowing for high-end precision everywhere from remote archaeological digs to active construction sites. Ultimately, these advancements help businesses and researchers save time, reduce costs, and preserve the world with unprecedented precision.
Guest Post by the SMARTTECH3D Team
Content and Images Provided by SMARTTECH3D Team



