Guest Post by Mr. Agastiya RV, BEACON, Technical Manager – Hyderabad
In any Electronic Enclosure, thermal management plays an important part of its design. The thermal design goal is to send the heat generated in the enclosure to the ambience. This can be achieved in many possible paths. In these paths, some of them can carry the heat easily and some other might develop a large resistance to the heat flow, due to the large temperature gradient, which creates a Bottleneck. This will also lead to the opportunity to introduce a Shortcut to the heat paths to avoid these bottlenecks.
The Bottleneck Bn and Shortcut Sc numbers are used primarily in electronics systems and other thermal systems. Hence, it’s a unique set of results that are exclusive for the Thermal Analysis in SOLIDWORKS Flow Simulation.
So, what exactly is a Bottleneck Number?
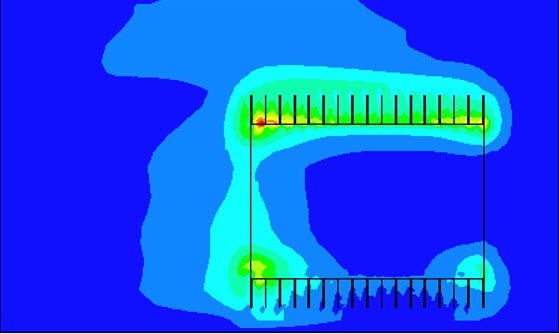
The Bottleneck number (Bn) identifies flow paths that carry high heat, while at the same time resist the flow of that heat. It is calculated by the ‘dot product’ of heat flux and temperature gradient vectors at any point.
Vector Notation:
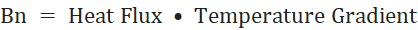
Scalar Notation:
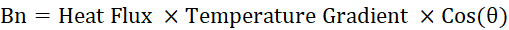
If the angle between the heat flux and temperature gradient is zero, then these two vectors are aligned with each other as it would be for conductive heat flow in a homogenous thermally isotropic material.
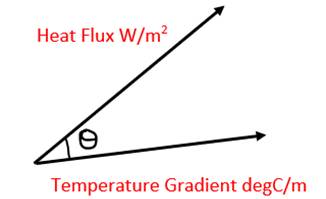
Vector Plot of Heat Flux and Temperature Gradient
The larger value of Bn is observed when:
- The heat flux is large
- And the temperature gradient is large
- And the two vectors align with each other
The large Bn is also observed when the heat experiences a resistance in the direction of heat flow.
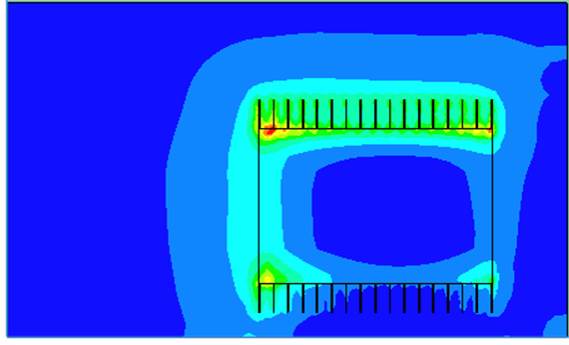
Bottleneck number Bn plot of a Heat Sink on a PCB
What is a Shortcut number?
The Shortcut number provides the opportunities for alternate and more efficient heat flow paths. It is calculated by the ‘cross product’ of Heat Flux and Temperature Gradient vectors at any point.
Vector Notation:

Scalar Notation:
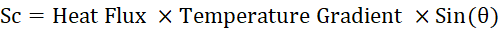
If the heat flux and temperature gradient are orthogonal to each other, then Sc is simply the product of vector magnitudes. The temperature gradient is taken to be the indication of an opportunity to divert the heat to cooler areas.
The larger value of Sc is observed when
- The heat flux is large
- The temperature gradient is large
- The two vectors are orthogonal
Large Sc is observed when the heat passes in parallel to a locally colder area.
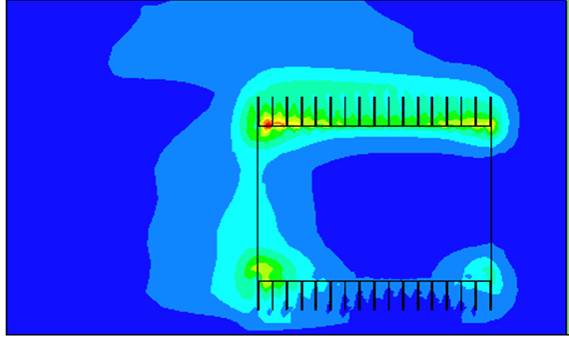
Shortcut number Sc of a Heat Sink on a PCB
Both Bottleneck Bn and Shortcut Sc numbers provides tremendous insights to the importance of thermal design analysis and the graphical information on where the design improvements are needed.
Bn provides us a clear insight of the thermal bottlenecks and Sc provides the information on introducing thermal shortcuts in the design.
Unlike parametric studies, Bn and Sc data provides us the physical insight, helping every thermal designer to make the designs at a faster pace and effectively. The identification and using these fields in an electronics design offers the most promising thermal design modifications.
Guest Post by Mr. Agastiya RV, BEACON, Technical Manager – Hyderabad
To know more details, please reach out to us at:
Phone: +91 7406663589
Email ID: info@beacon-india.com Website: http://beacon-india.com